PLANTS TO GROW FOR BEAUTIFUL GARDENS AND STUNNING ARRANGEMENTS
With the Garden Club of Virginia’s annual Historic Garden Week tours upon us, here are a few suggestions for plants you can grow and use in arrangements like those you see on tour. I highlight four arrangements here that were created for last year’s tour by the talented gardeners and arrangers Susan Robertson, Margy Brown, Ida Farinholt, Sally Ellington and Gretchn Japhet. Almost all of the plants used in the arrangements came from their own and others’ gardens.
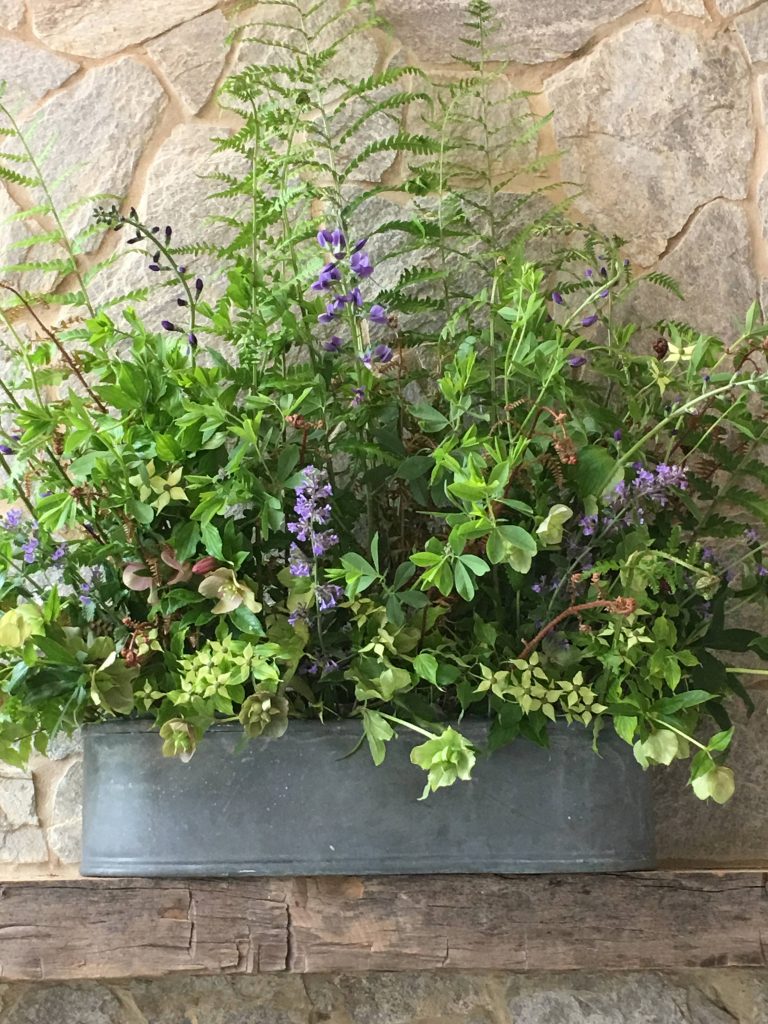

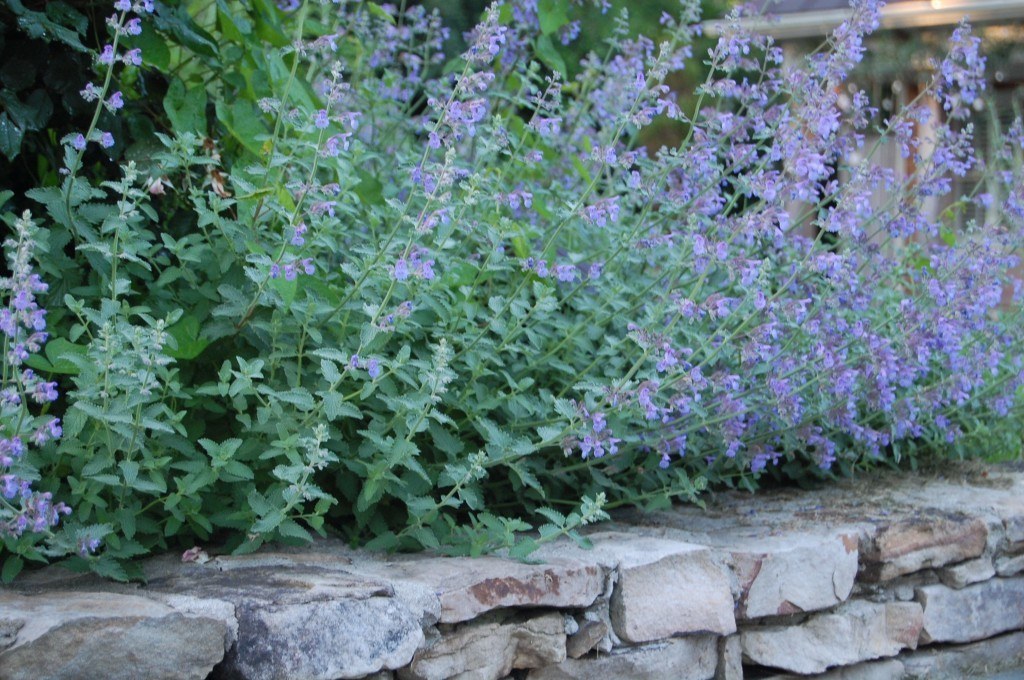
The mantel arrangement above is like a Virginia spring garden that snuck indoors. The backdrop of the stone wall, rough hewn timber mantel and simple galvanized metal container is perfect for the natural arrangement displaying many native plants. Included in the arrangement are false indigo (Baptisia australis, native), kousa dogwood (Cornus kousa — it’s cousin, Cornus florida, is native), lenten rose (Helleborus orientalis), dixie wood fern (Dryopteris x australis, native), Autumn Fern (Dryopteris erythrosora), the foliage of coral honeysuckle (Lonicera sempervirens, native) and Catmint (Nepeta x faassenii).
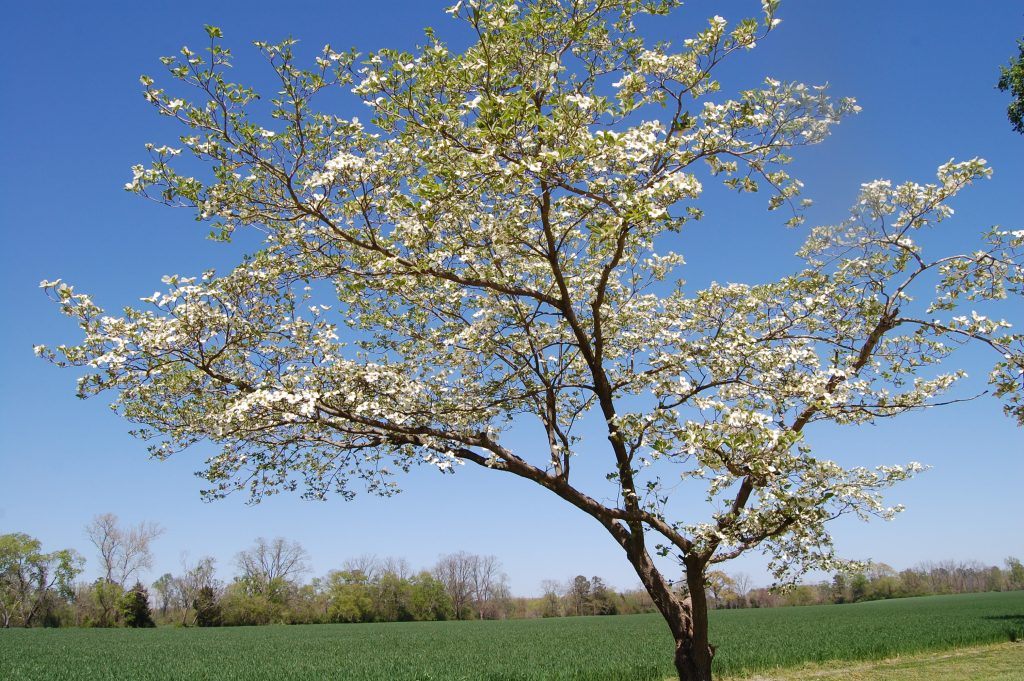 Kousa dogwood was used in the arrangement, but the native flowering dogwood, which flowers earlier and before it leafs out, is a fantastic choice for your garden. Kousa dogwood, native to China, supports no insect herbivores. Our native dogwood supports 117 species of moth and caterpillar as well as many other insects. http://www.bringingnaturehome.net/gardening-for-life.html
Kousa dogwood was used in the arrangement, but the native flowering dogwood, which flowers earlier and before it leafs out, is a fantastic choice for your garden. Kousa dogwood, native to China, supports no insect herbivores. Our native dogwood supports 117 species of moth and caterpillar as well as many other insects. http://www.bringingnaturehome.net/gardening-for-life.html
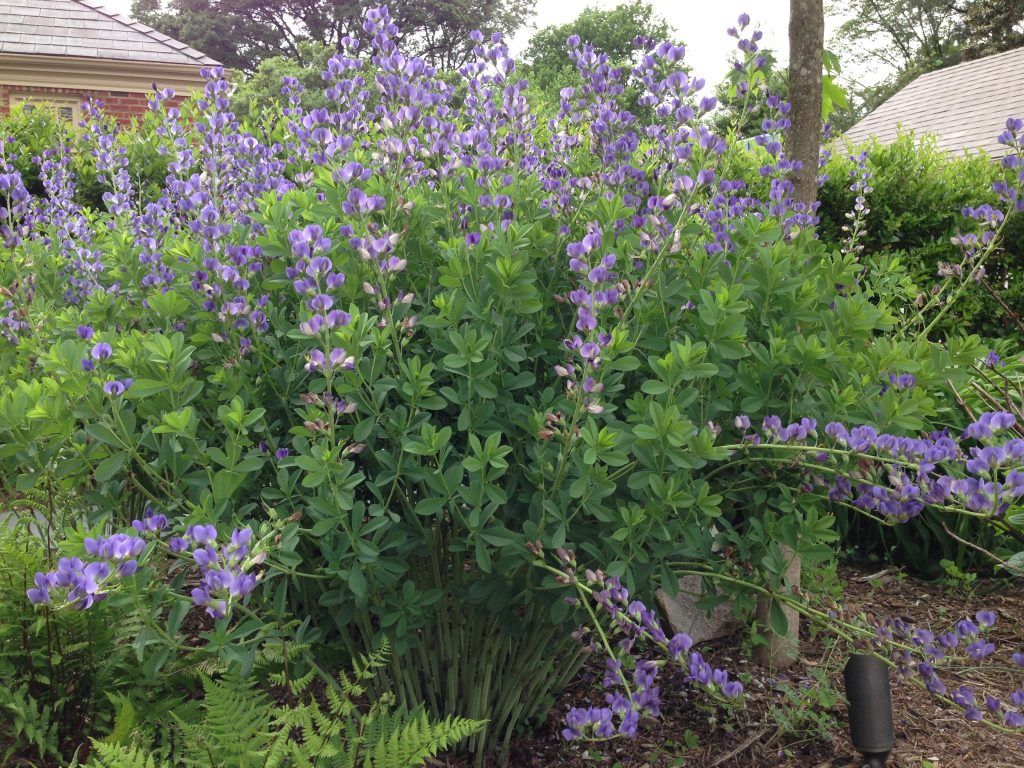 False Indigo, with its sweet pea-like flowers, is native, prefers part sun, and is attractive for its foliage and bloom.
False Indigo, with its sweet pea-like flowers, is native, prefers part sun, and is attractive for its foliage and bloom.
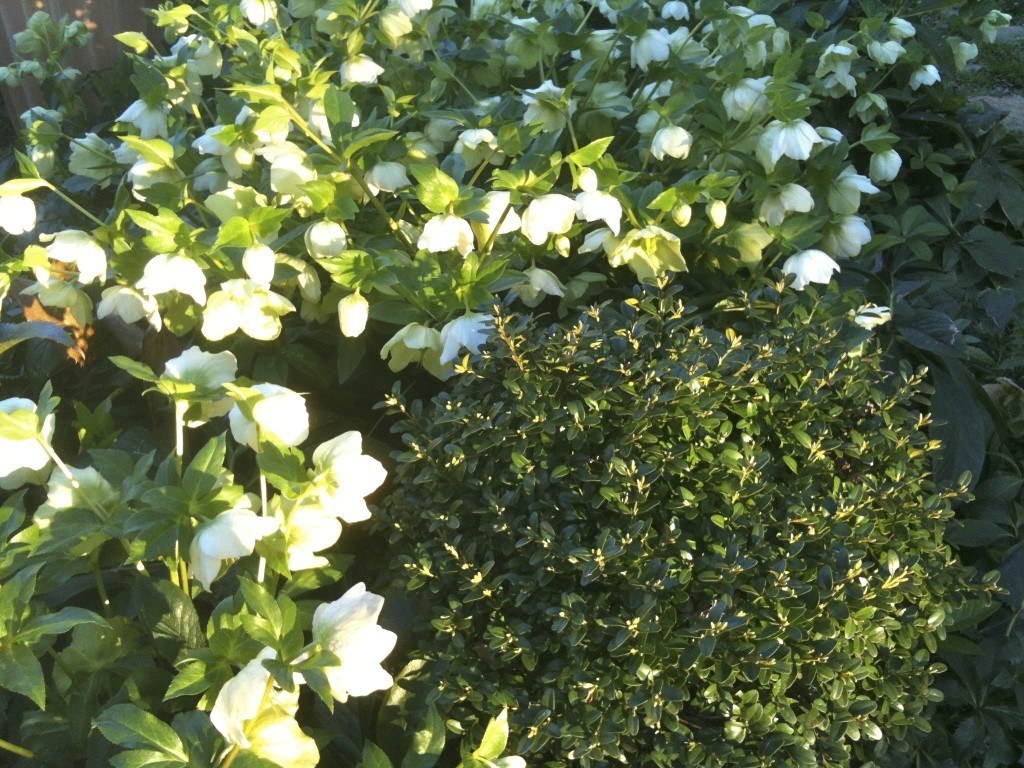
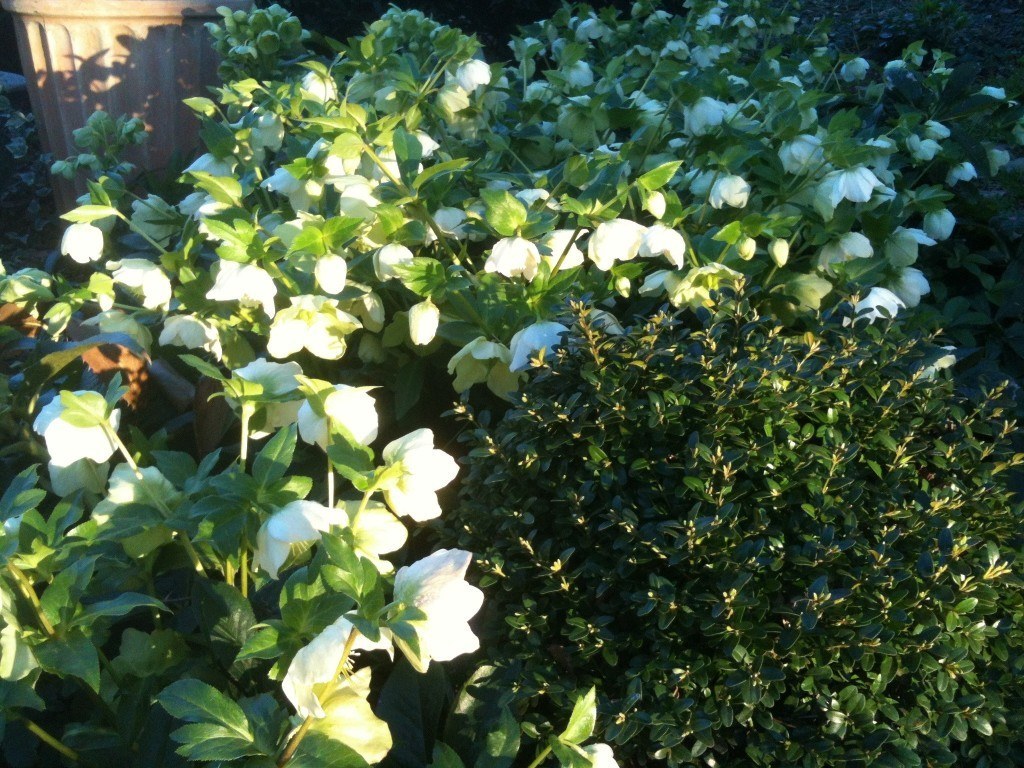
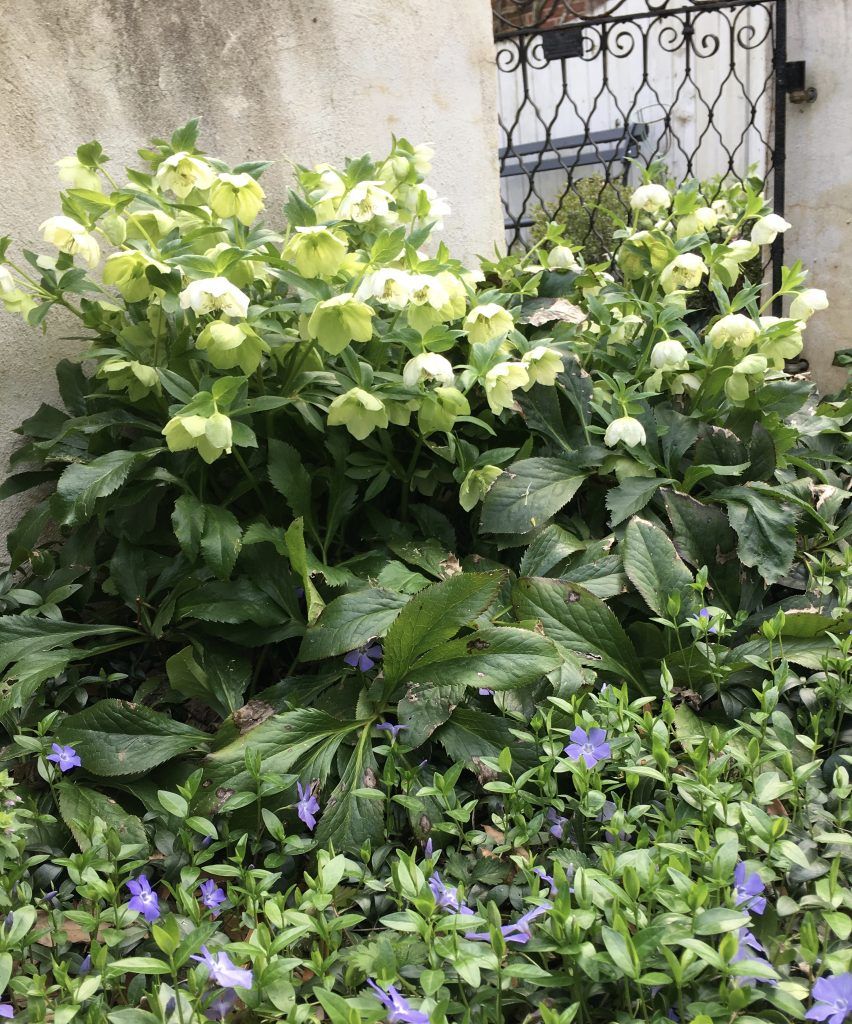 Lenten Rose is one of my favorite plants. It is evergreen, the blooms (actually the bracts), persist for up to three or four months, and it happily, but not aggressively, self-seeds. It is happiest in part shade or shade.
Lenten Rose is one of my favorite plants. It is evergreen, the blooms (actually the bracts), persist for up to three or four months, and it happily, but not aggressively, self-seeds. It is happiest in part shade or shade.
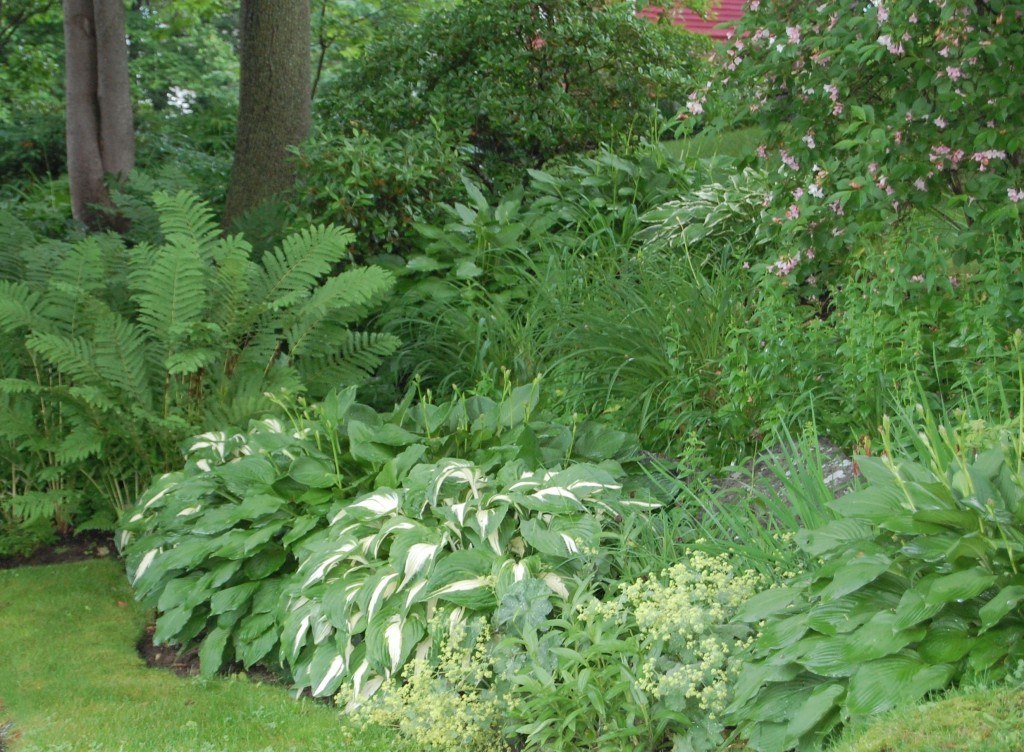
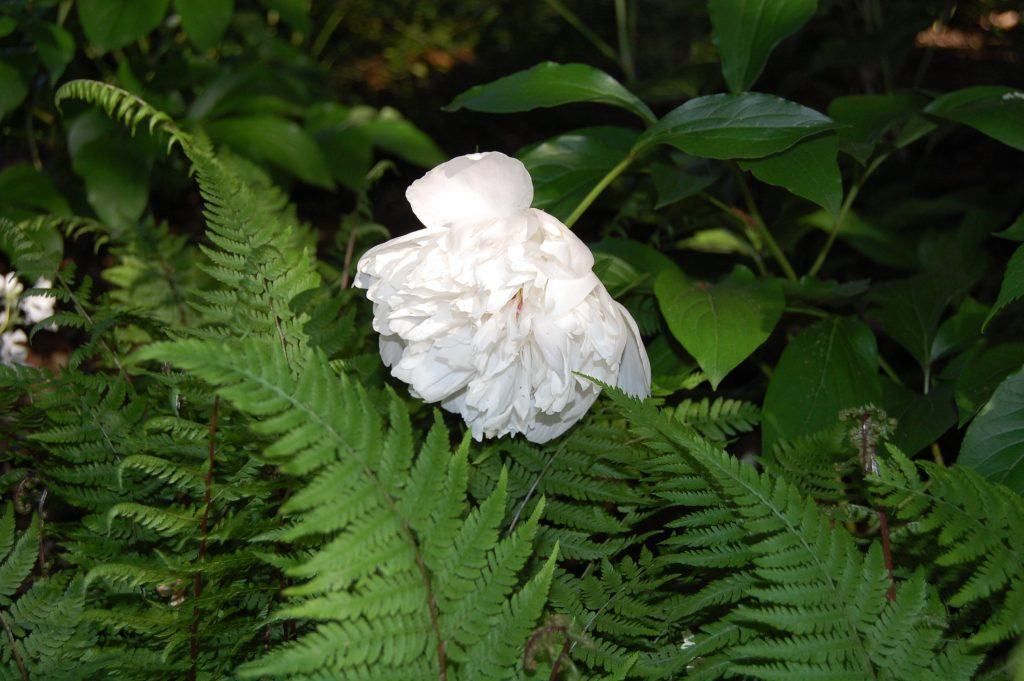 The native Dixie wood fern and the young (red) fiddlers of autumn fern were used in the arrangement. Another lovely fern, which is native, is Lady Fern (Athyrium filix-femina). It is more delicate than most ferns, but provides an airy sweep in the garden.
The native Dixie wood fern and the young (red) fiddlers of autumn fern were used in the arrangement. Another lovely fern, which is native, is Lady Fern (Athyrium filix-femina). It is more delicate than most ferns, but provides an airy sweep in the garden.
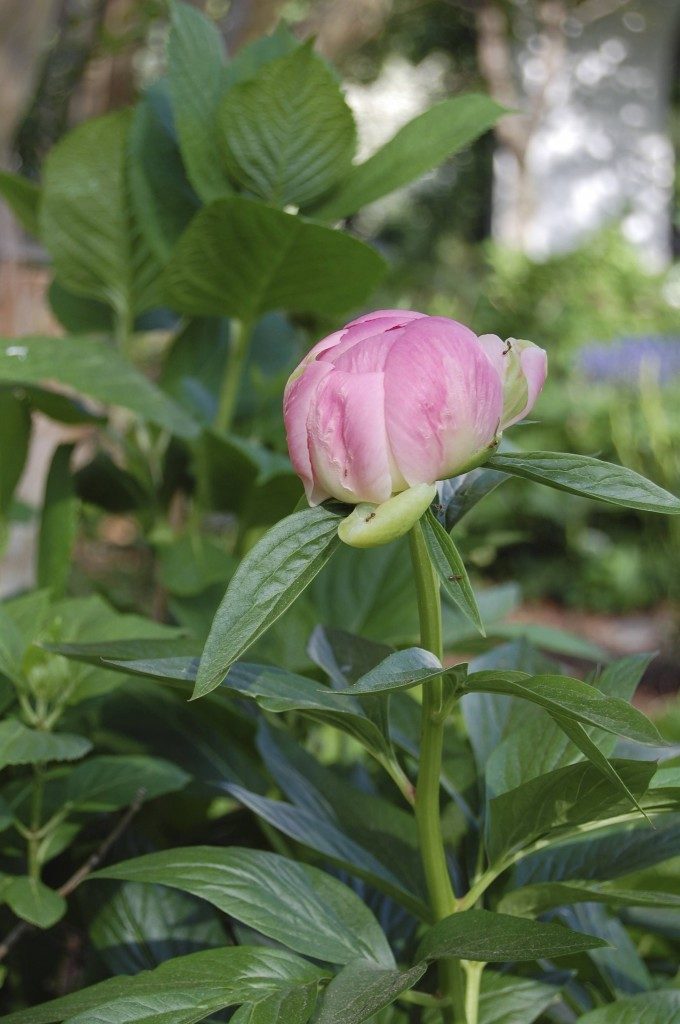
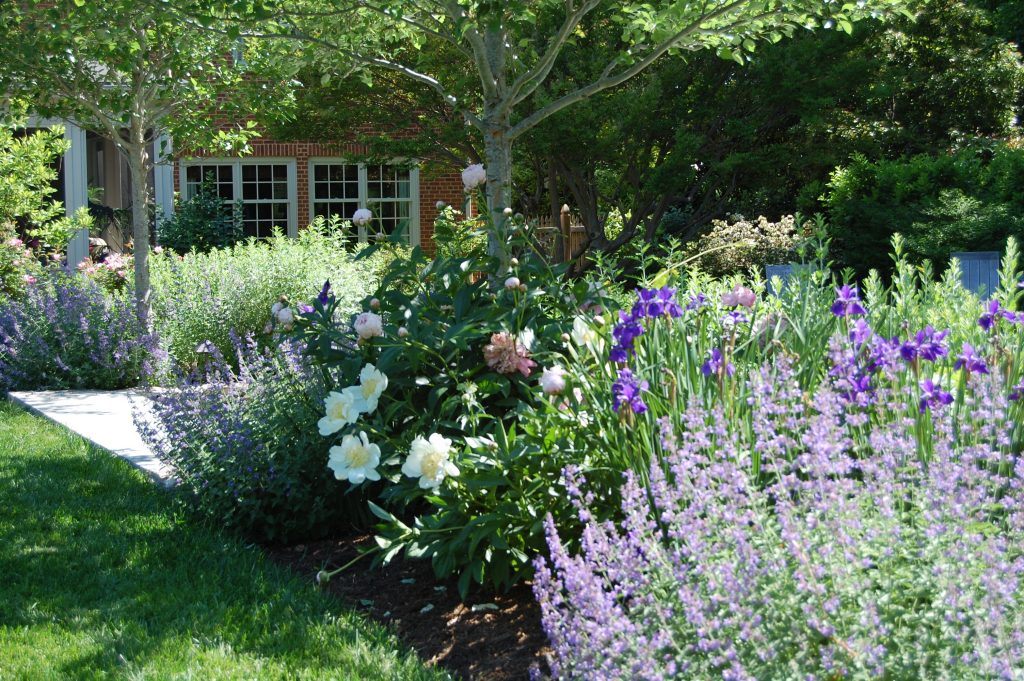
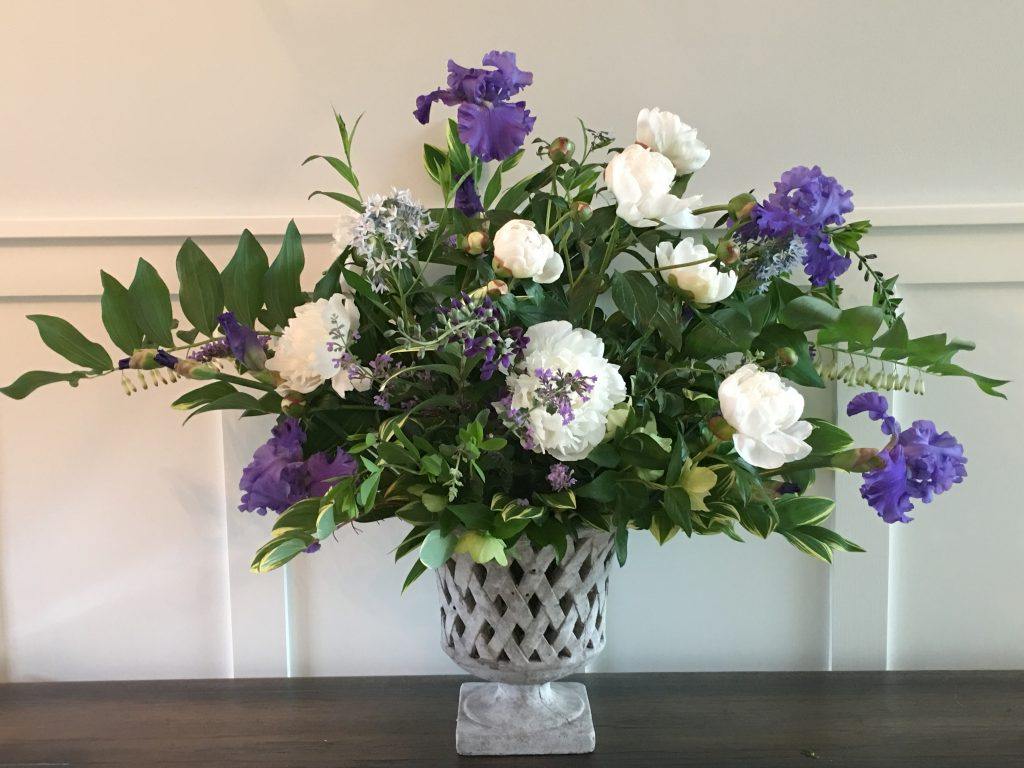 The greens in the arrangement above allow the spectacular peonies (Paeonia latifolia) and bearded iris (Iris germanica) to stand out. Supporting players are both the native solomon’s seal (Polygonatum biflorum var. commutatum and it’s variegated cousin (Polygonatum odoratum var. pluriflorum ‘Variegatum’), false indigo, lenten rose, and blue star (Amsonia tabernaemontana).
The greens in the arrangement above allow the spectacular peonies (Paeonia latifolia) and bearded iris (Iris germanica) to stand out. Supporting players are both the native solomon’s seal (Polygonatum biflorum var. commutatum and it’s variegated cousin (Polygonatum odoratum var. pluriflorum ‘Variegatum’), false indigo, lenten rose, and blue star (Amsonia tabernaemontana).
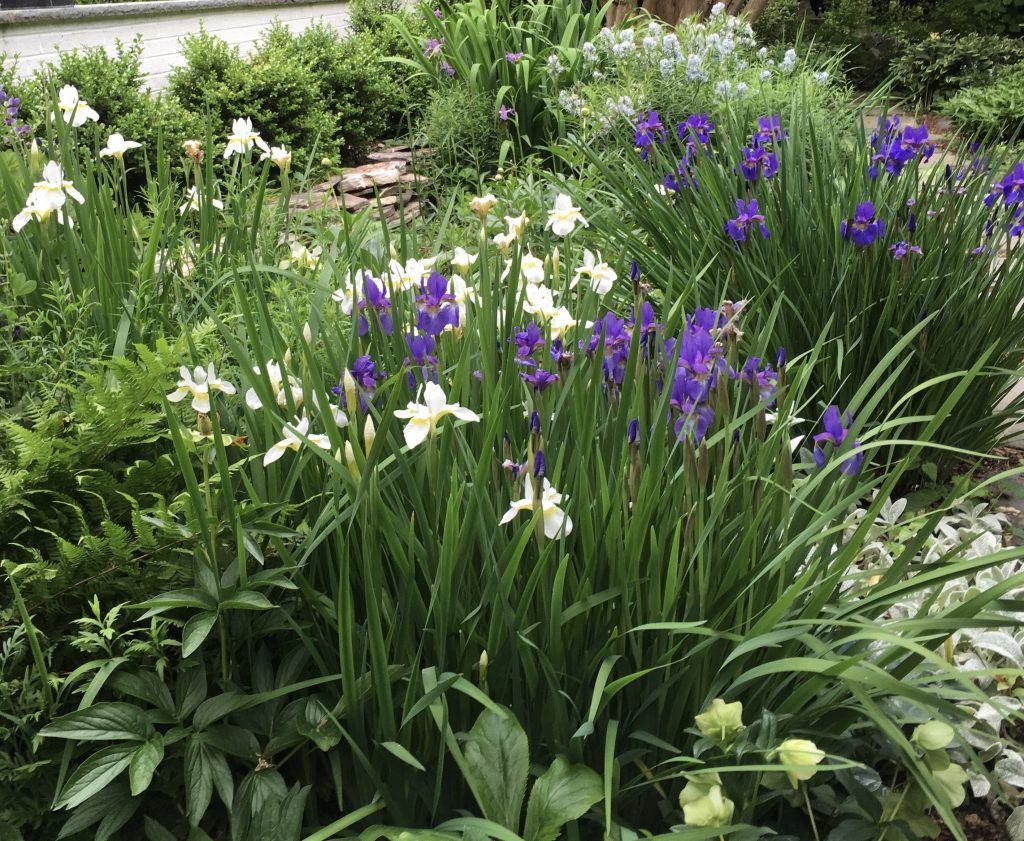 The iris used in the arrangement is bearded iris. Above are two siberian iris cultivars (Iris siberica ‘Caesar’s Brother’ and ‘Butter and Sugar’). Siberian iris, as well as the native blue flag iris (Iris versicolor) will tolerate wet soil conditions. The sword-like foliage provides nice structure in the perennial border when the plant is not in bloom.
The iris used in the arrangement is bearded iris. Above are two siberian iris cultivars (Iris siberica ‘Caesar’s Brother’ and ‘Butter and Sugar’). Siberian iris, as well as the native blue flag iris (Iris versicolor) will tolerate wet soil conditions. The sword-like foliage provides nice structure in the perennial border when the plant is not in bloom.
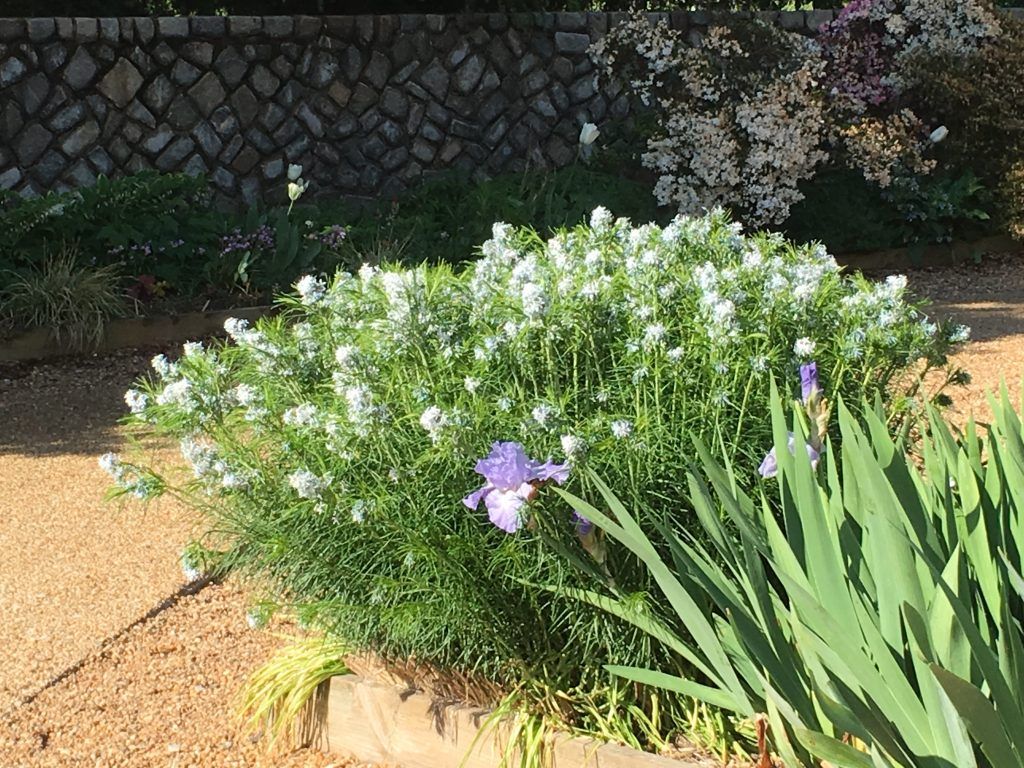

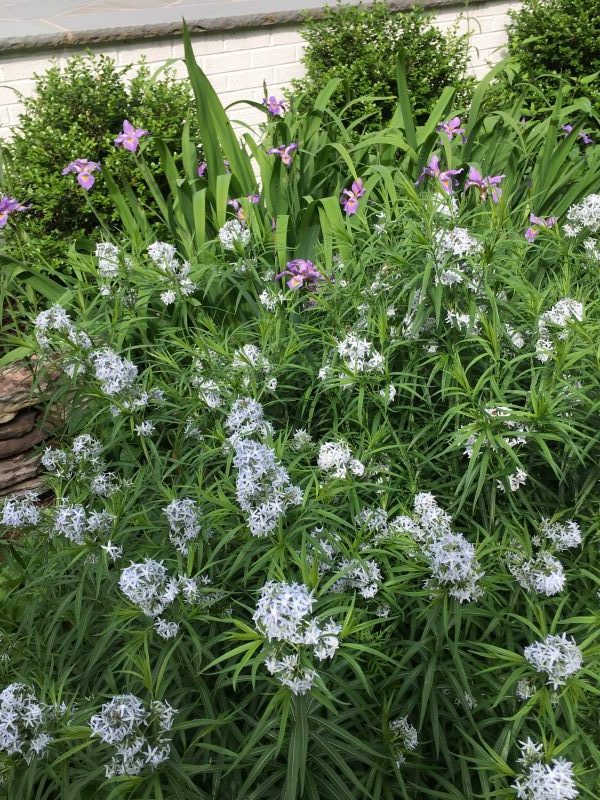
Amsonia hubrichtii (threadleaf bluestar) is pictured above. The native Amsonia tabernaemontana (eastern bluestar) is pictured below with the native blue flag iris). A. hubrichtii has spectacular yellow fall foliage. Amsonias tolerate full sun to part shade, and benefit from having their foliage cut by 1/3 to 1/2 after blooming for less floppy foliage (the foliage will continue to grow).
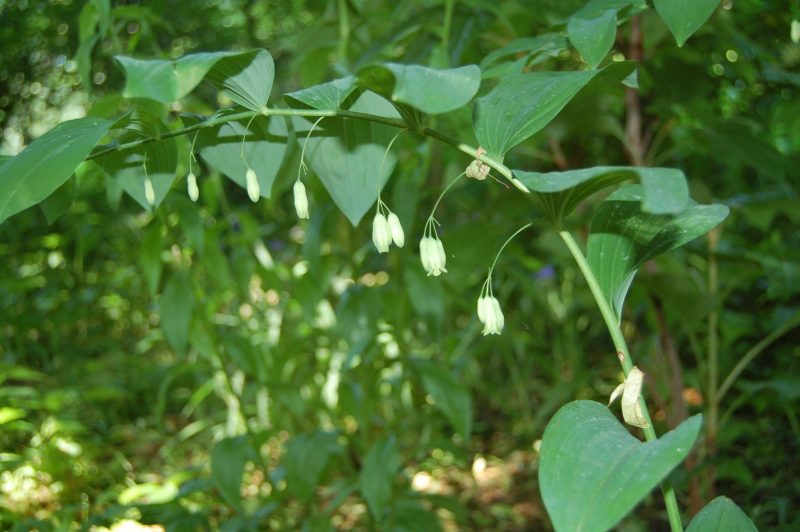


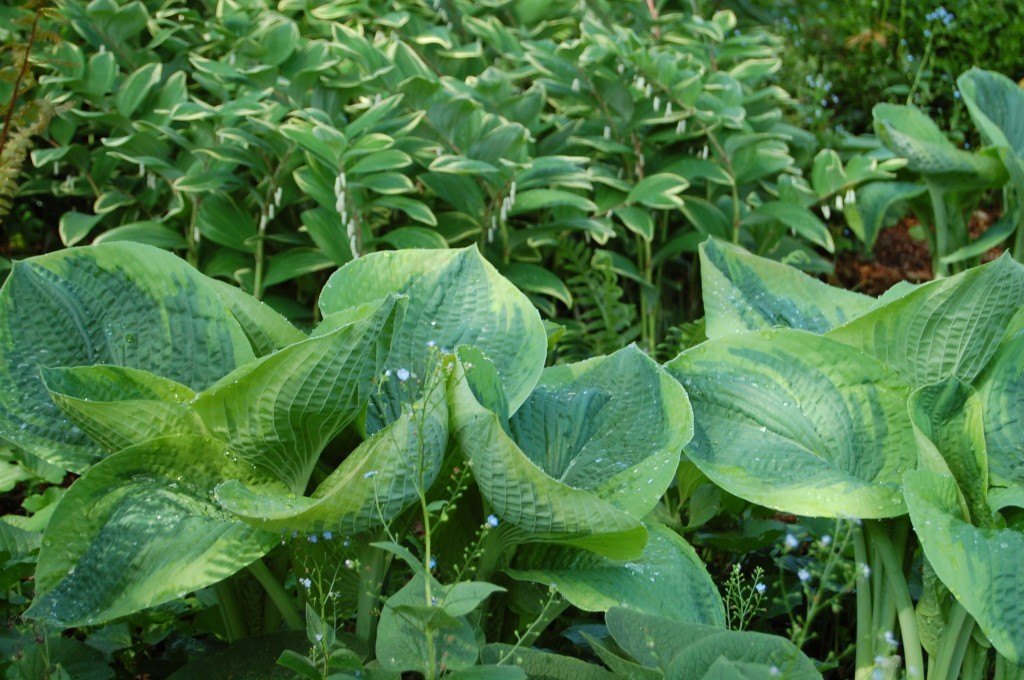
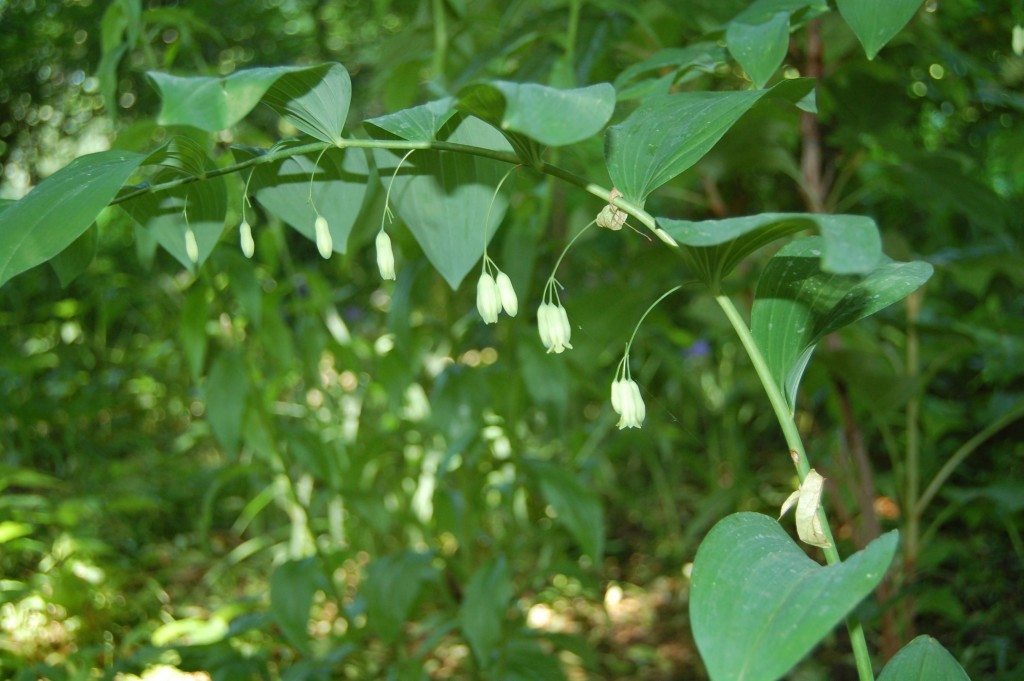
The native Giant Solomon’s Seal, Polygonatum biflorum var. commutatum, can be found in Richmond’s James River Park System. It will tolerate wet soil and prefers shade.
 These bottle bud vases are such a great way to remove the stress of arranging and make use of the bounty of the garden at any given time in the growing season. Early cottage roses and tulips join the catmint, lenten rose and greens for a lovely tableau.
These bottle bud vases are such a great way to remove the stress of arranging and make use of the bounty of the garden at any given time in the growing season. Early cottage roses and tulips join the catmint, lenten rose and greens for a lovely tableau. Single tulips underplanted with violas.
Single tulips underplanted with violas.
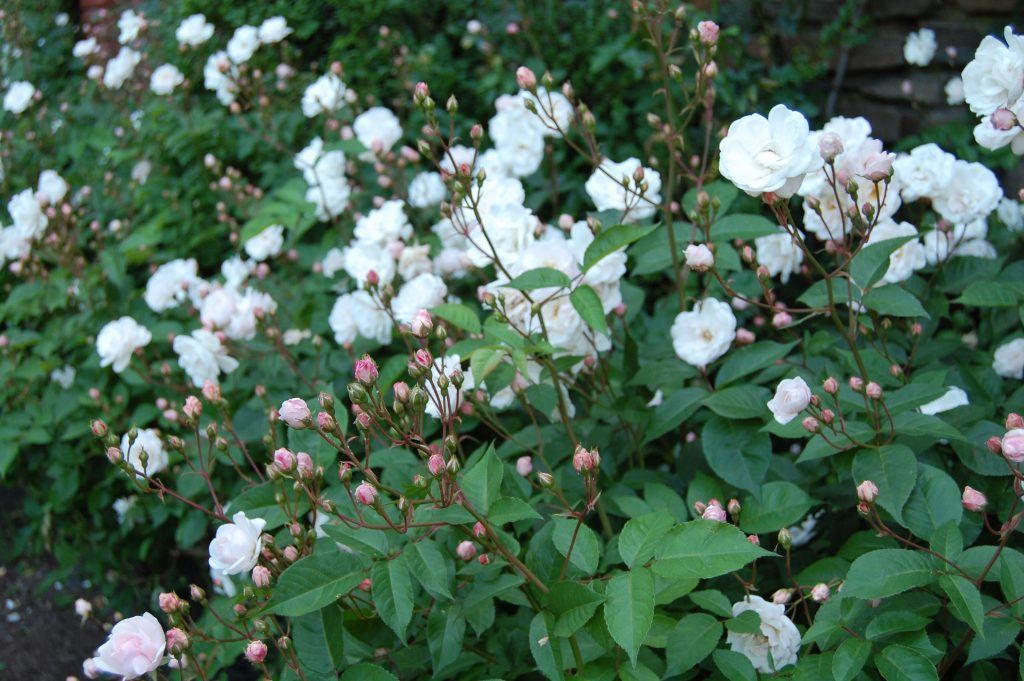 The roses above are in the gardens of Dumbarton Oaks. I’m not sure of the species.
The roses above are in the gardens of Dumbarton Oaks. I’m not sure of the species.
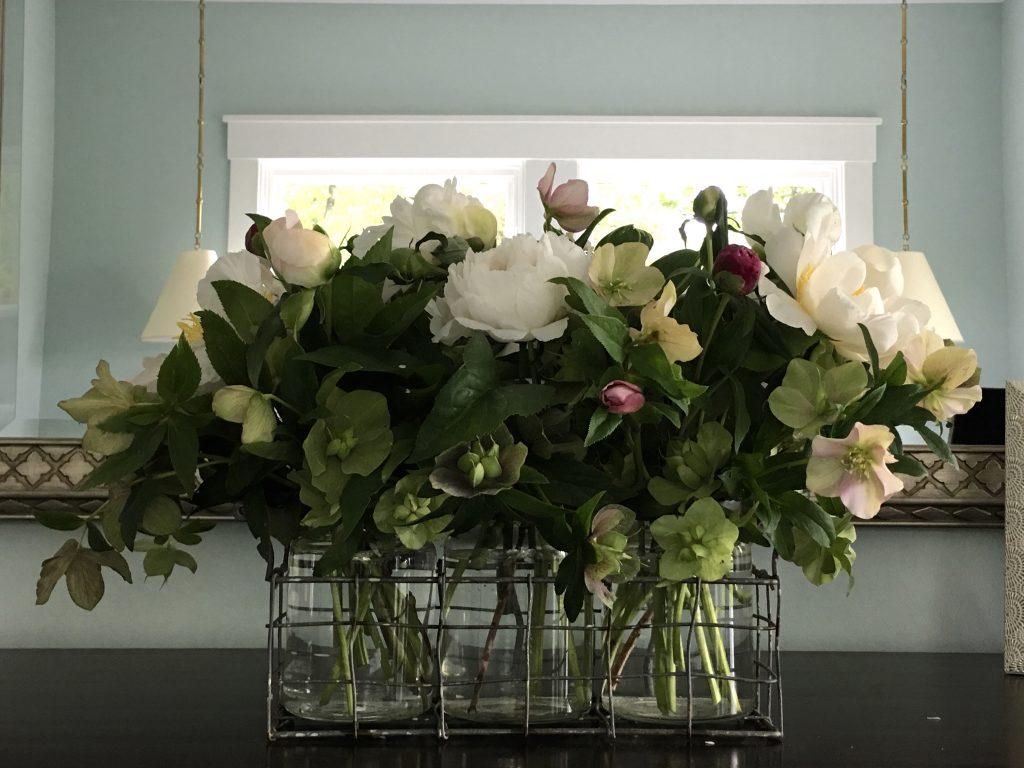 The arrangers took advantage of last year’s early spring, using these gorgeous, billowy peonies, and masterly pulling out the subtle deep and soft pinks of the lenten roses and peony buds.
The arrangers took advantage of last year’s early spring, using these gorgeous, billowy peonies, and masterly pulling out the subtle deep and soft pinks of the lenten roses and peony buds.
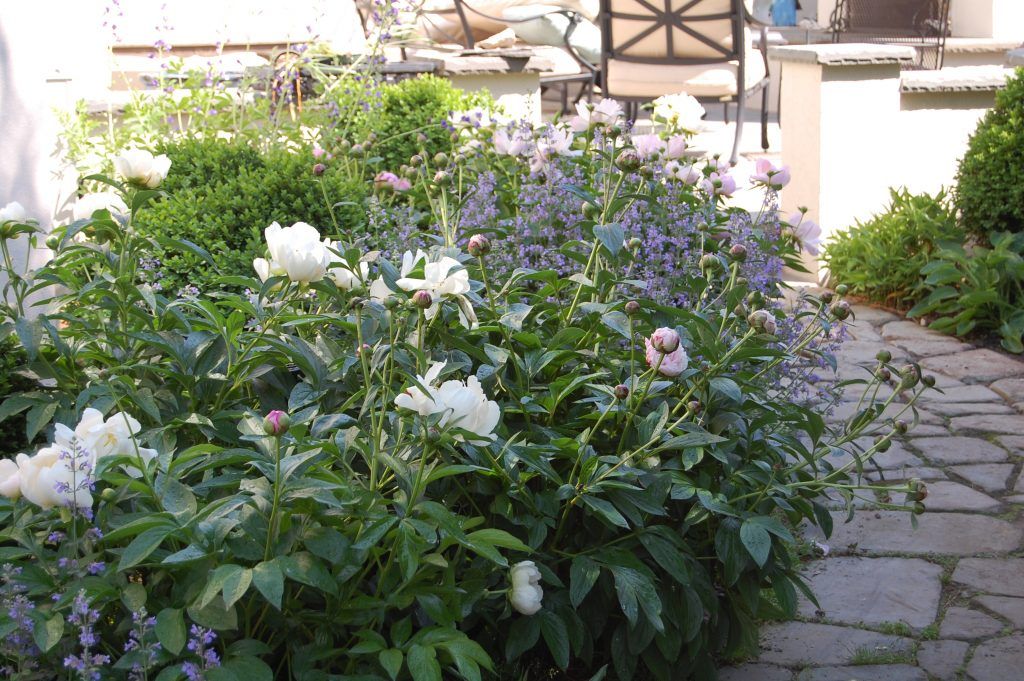

Peonies intermingle happily with catmint, false indigo and boxwood.
[custom-related-posts title=”Related Posts” none_text=”None found” order_by=”title” order=”ASC”]
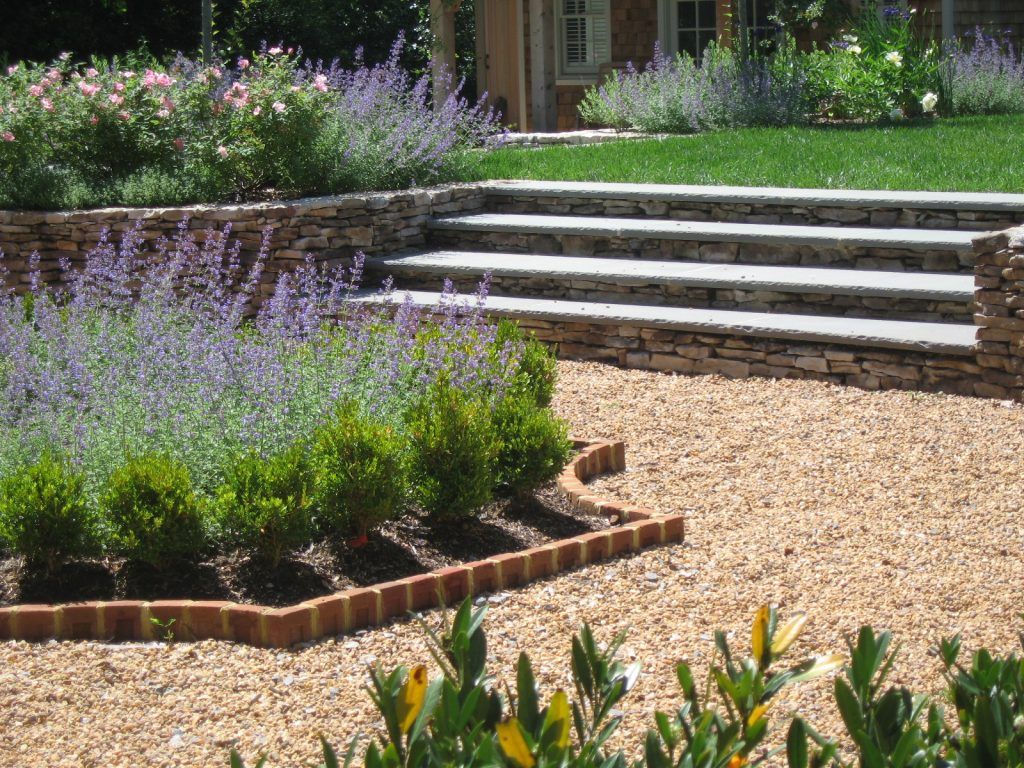





















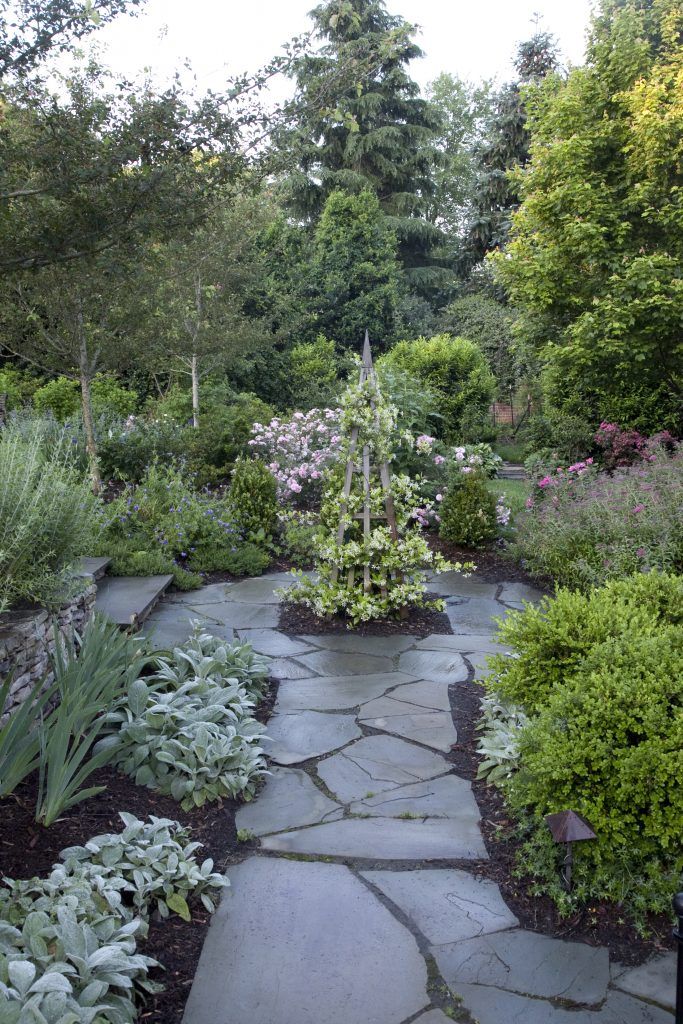
 The new brick garage (which replaced the wood shed) and brick wall provide a sense of enclosure for the backyard. The planting beds are edged in brick in what I call a Gillette border.
The new brick garage (which replaced the wood shed) and brick wall provide a sense of enclosure for the backyard. The planting beds are edged in brick in what I call a Gillette border.
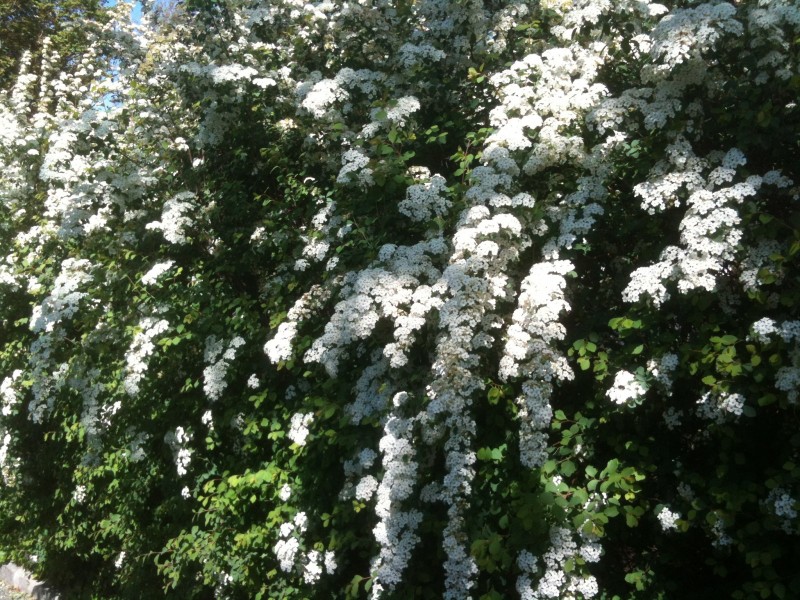
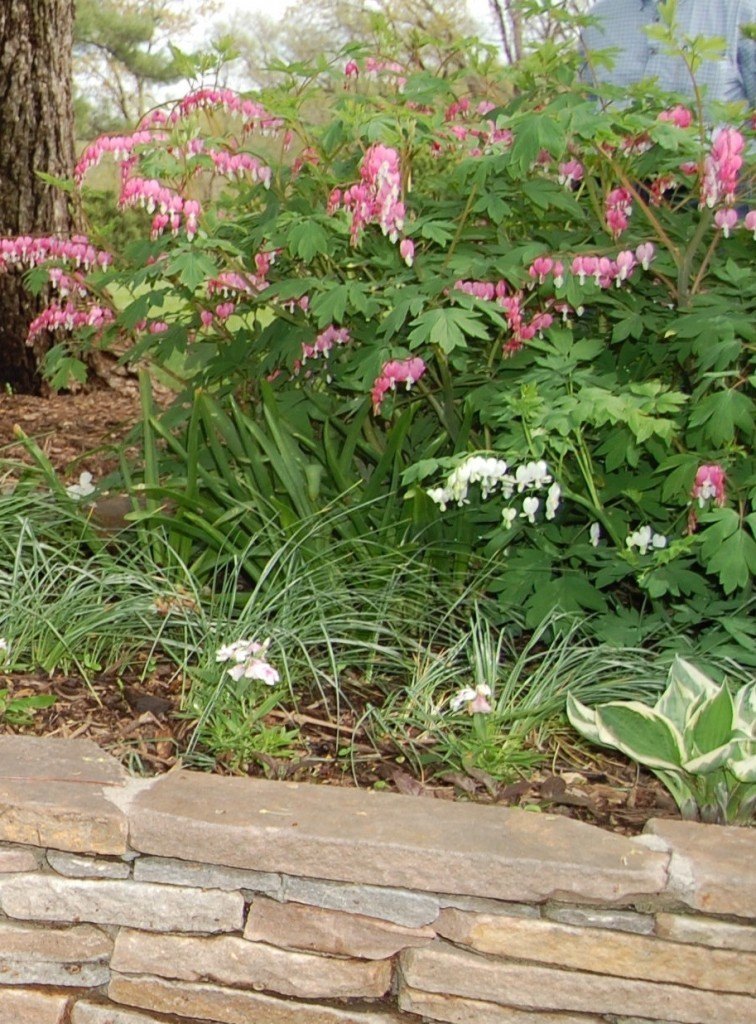
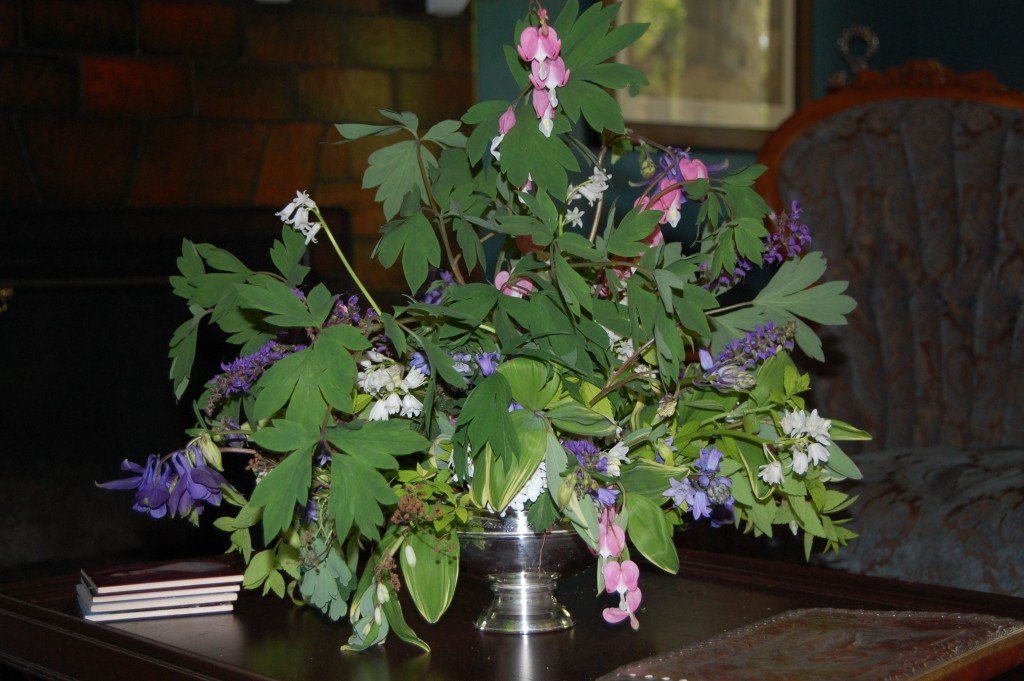
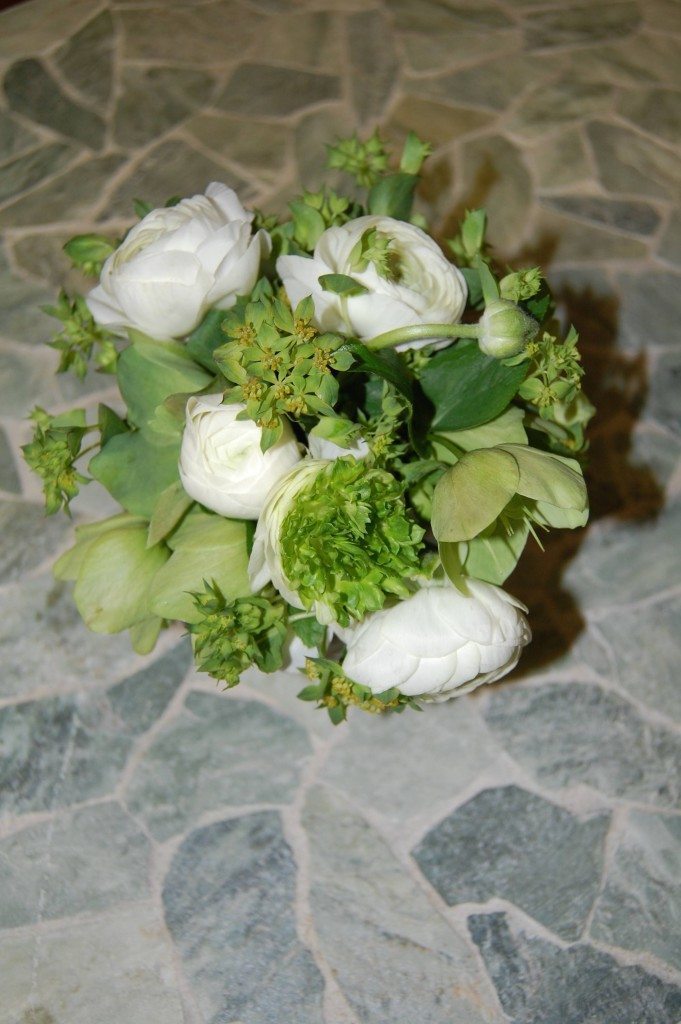
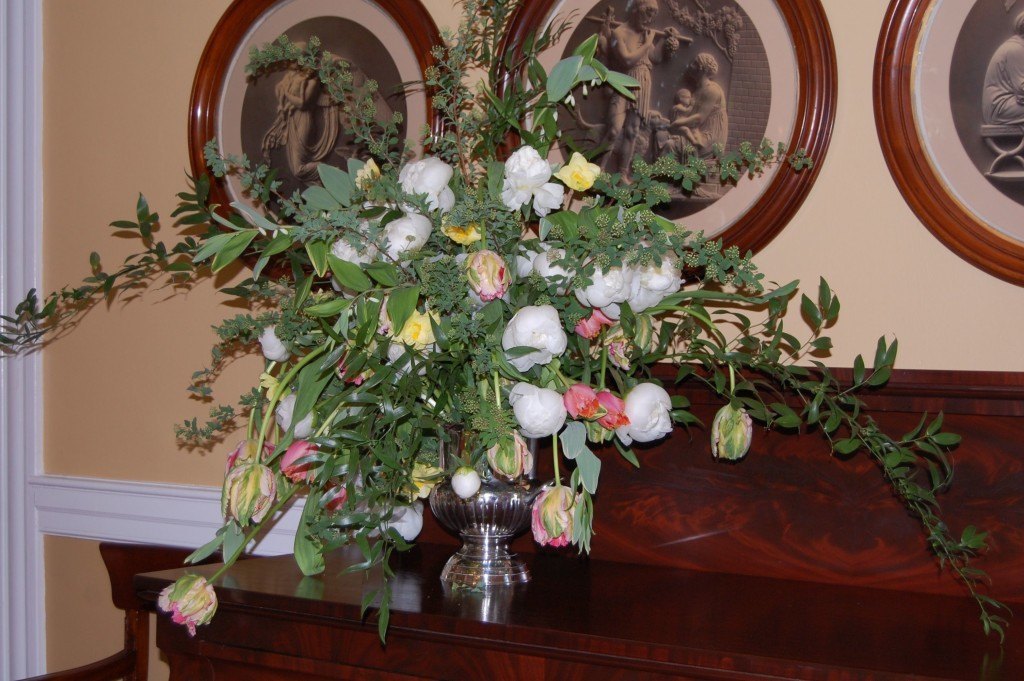












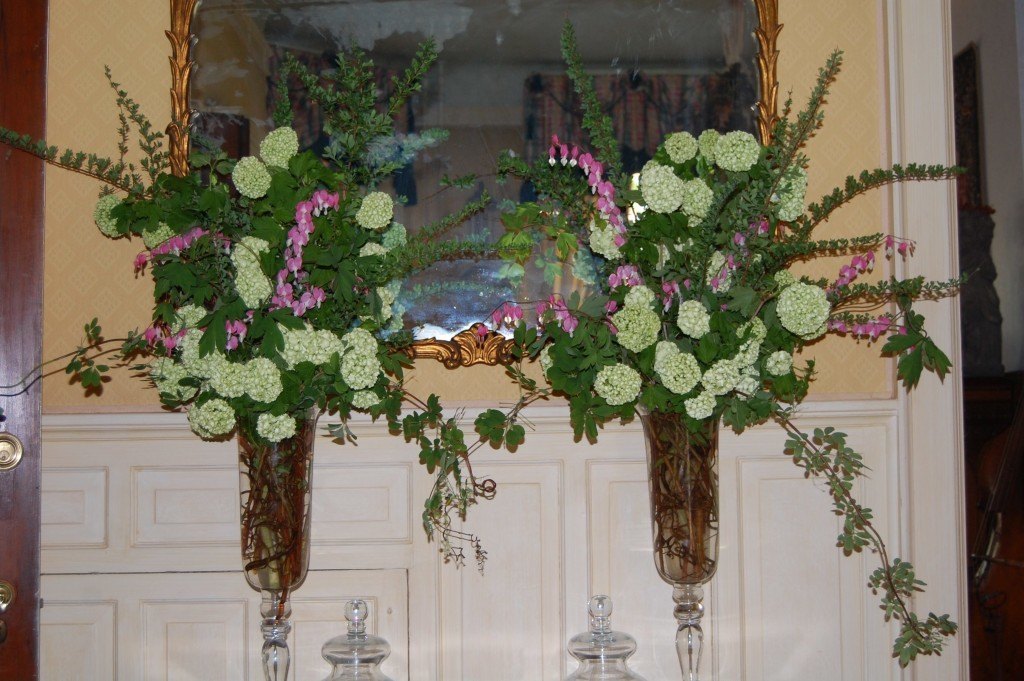












 The dramatic arrangement above includes the Spirea and Solomon’s Seal pictured earlier, but the leading ladies here are the Parrot Tulips taking a bow. Poet’s Laurel (Danae racemosa) and Ranunculus anchor the arrangement.
The dramatic arrangement above includes the Spirea and Solomon’s Seal pictured earlier, but the leading ladies here are the Parrot Tulips taking a bow. Poet’s Laurel (Danae racemosa) and Ranunculus anchor the arrangement.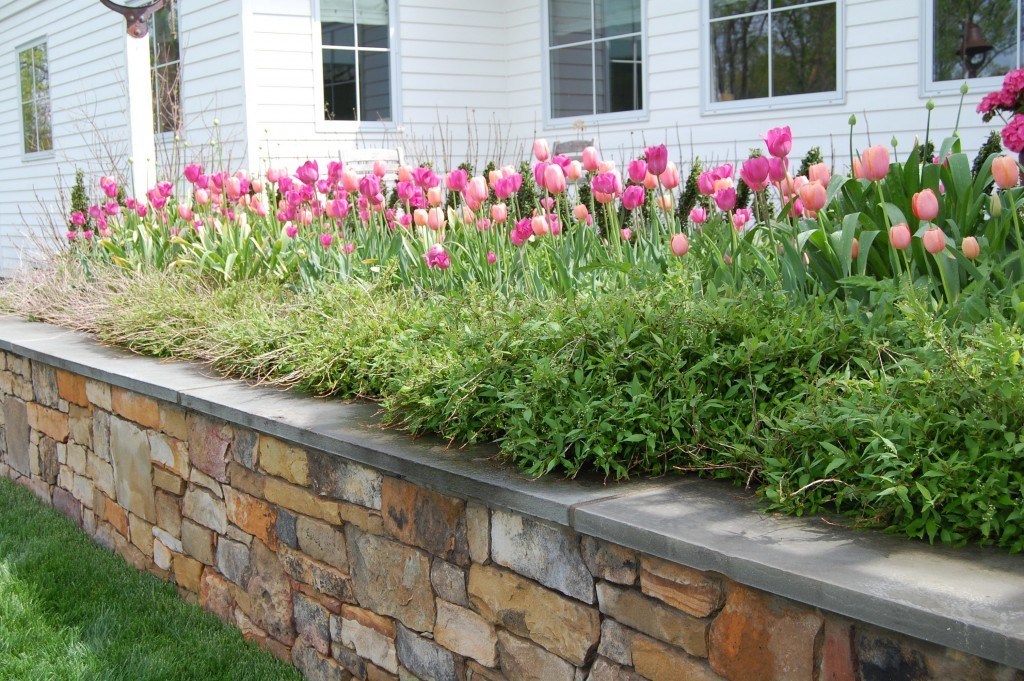
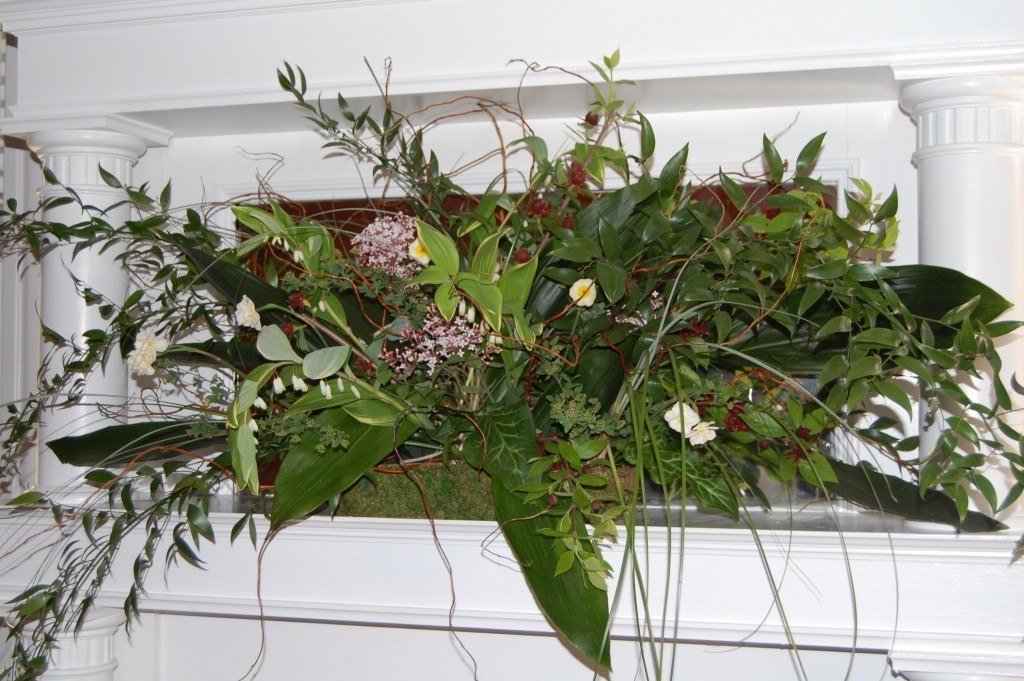



 This modern arrangement has an abundance of greenery, including grasses, Poet’s Laurel, Variegated Solomon’s Seal and Arum (Arum italica). Flowers are used sparingly, but to great effect. They include dimuntive daffodil blooms, Lilac (Syringa, genus, I think it is ‘Miss Kim’), and Carolina Allspice (Calycanthus floridus).
This modern arrangement has an abundance of greenery, including grasses, Poet’s Laurel, Variegated Solomon’s Seal and Arum (Arum italica). Flowers are used sparingly, but to great effect. They include dimuntive daffodil blooms, Lilac (Syringa, genus, I think it is ‘Miss Kim’), and Carolina Allspice (Calycanthus floridus).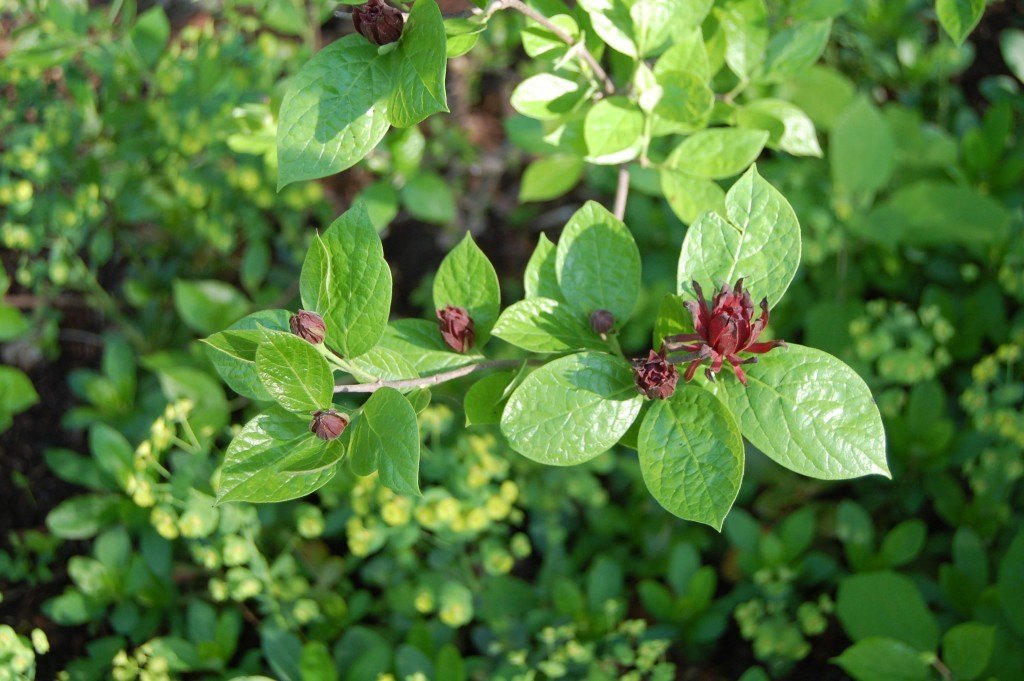
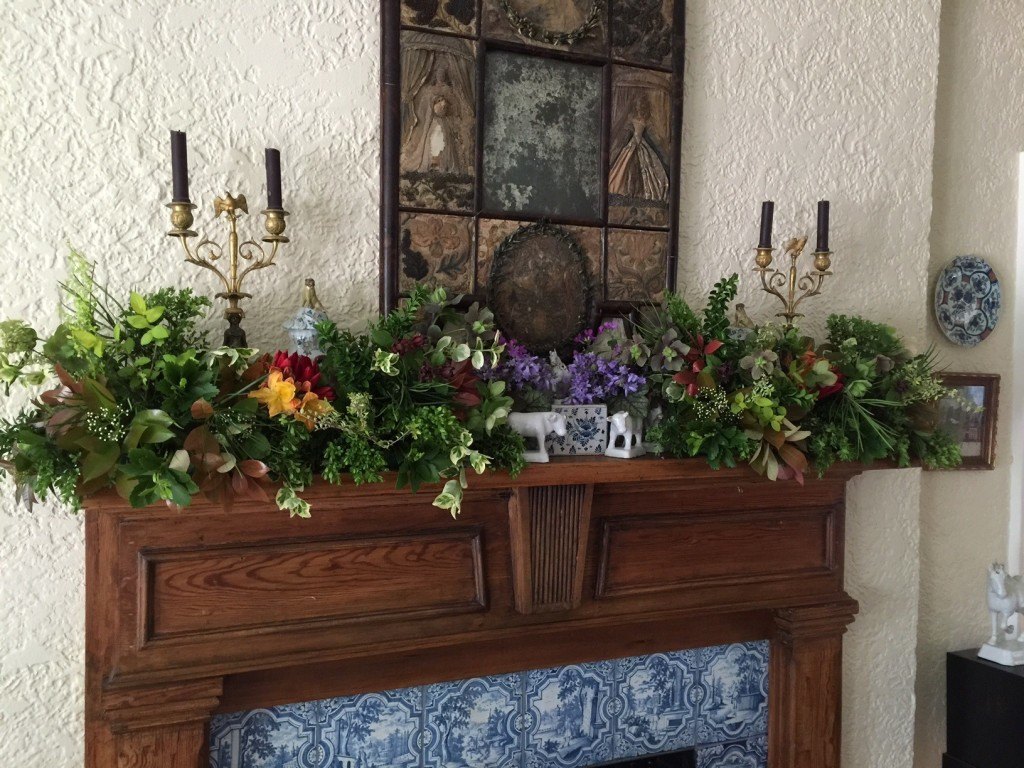
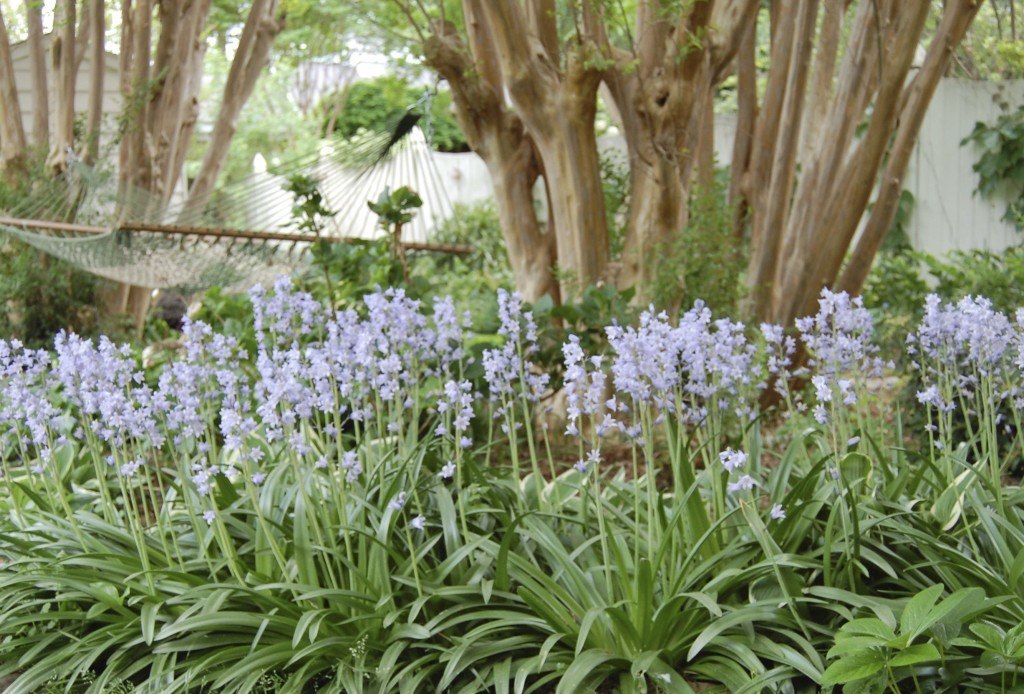
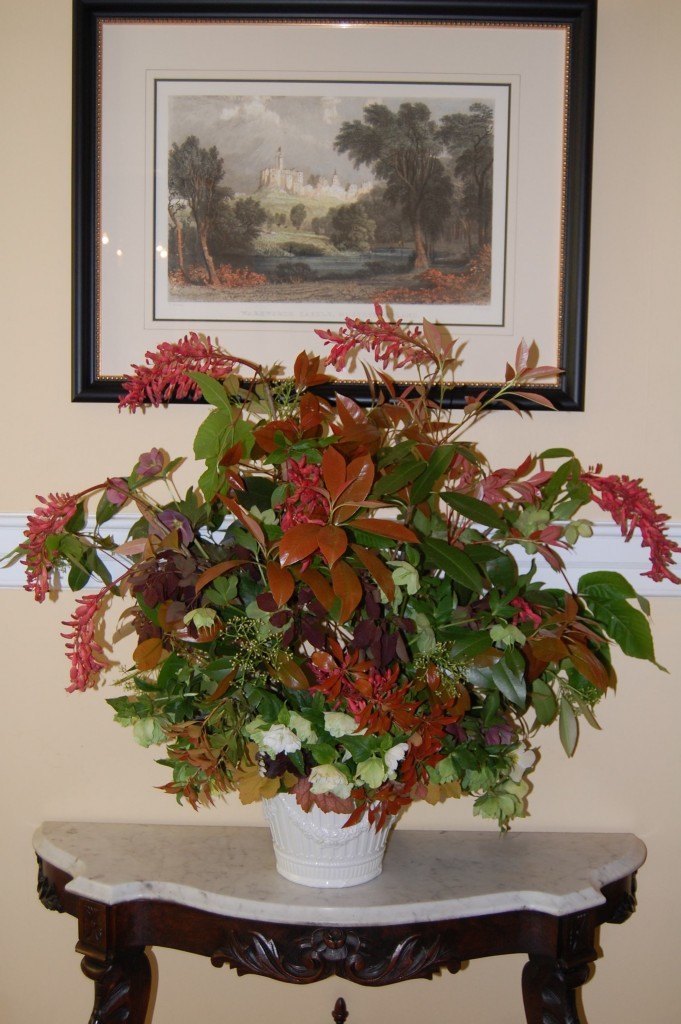
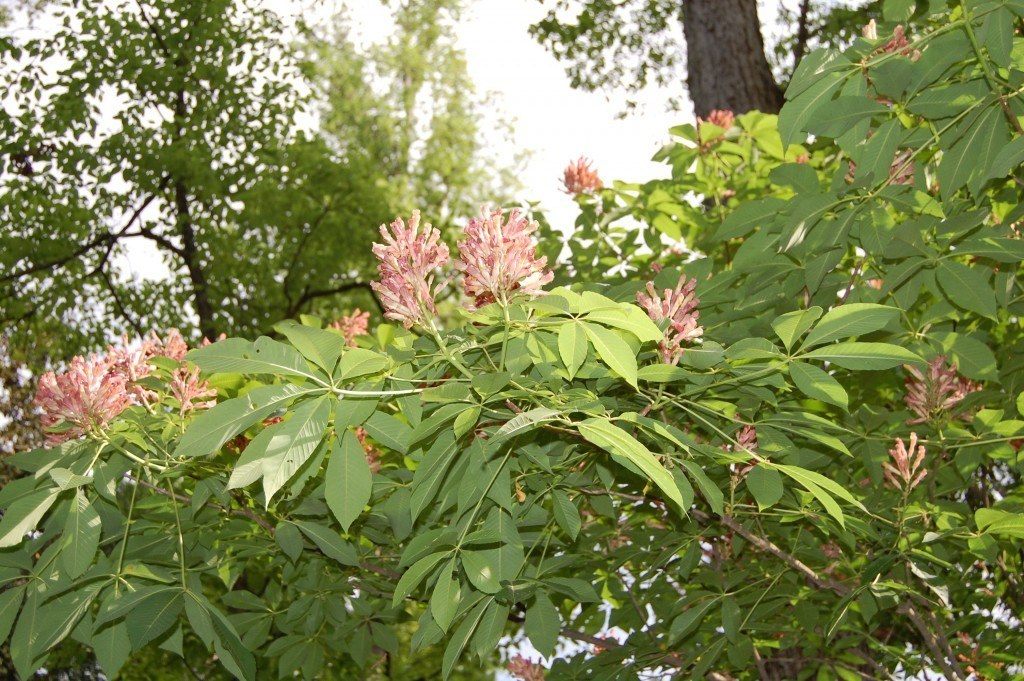
 The mantle arrangement above is a feast of textures and contrasting hues, with Photinia, Boxwood, Variegated Euonymus, Spanish Bluebells, Lenten Rose, Pachysandra and Native Azalea. Photo by Betsy Trow.
The mantle arrangement above is a feast of textures and contrasting hues, with Photinia, Boxwood, Variegated Euonymus, Spanish Bluebells, Lenten Rose, Pachysandra and Native Azalea. Photo by Betsy Trow.
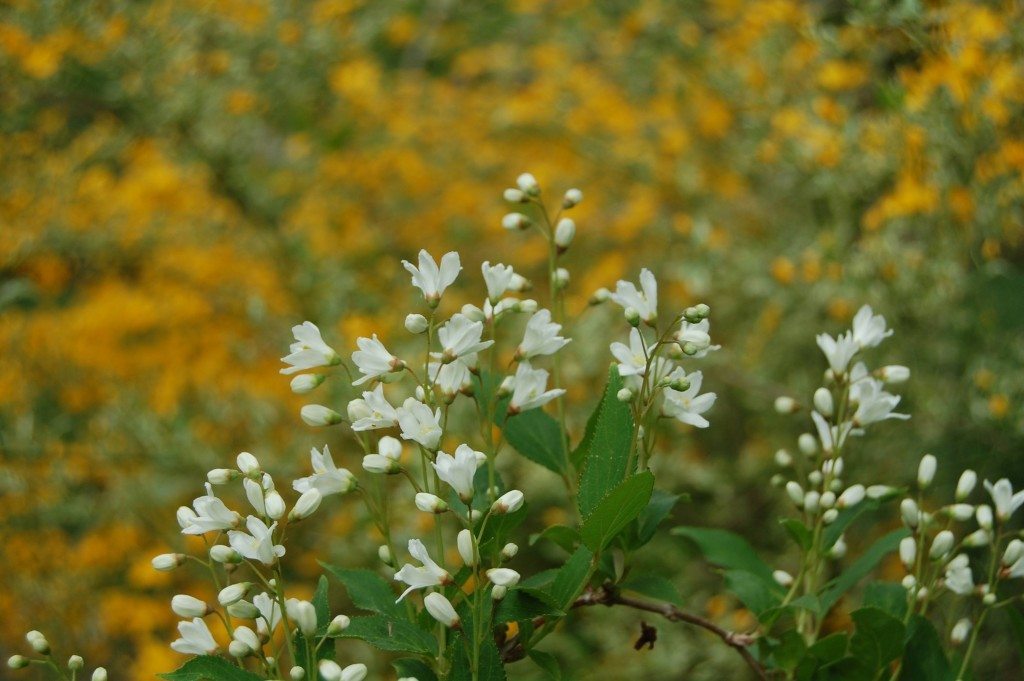
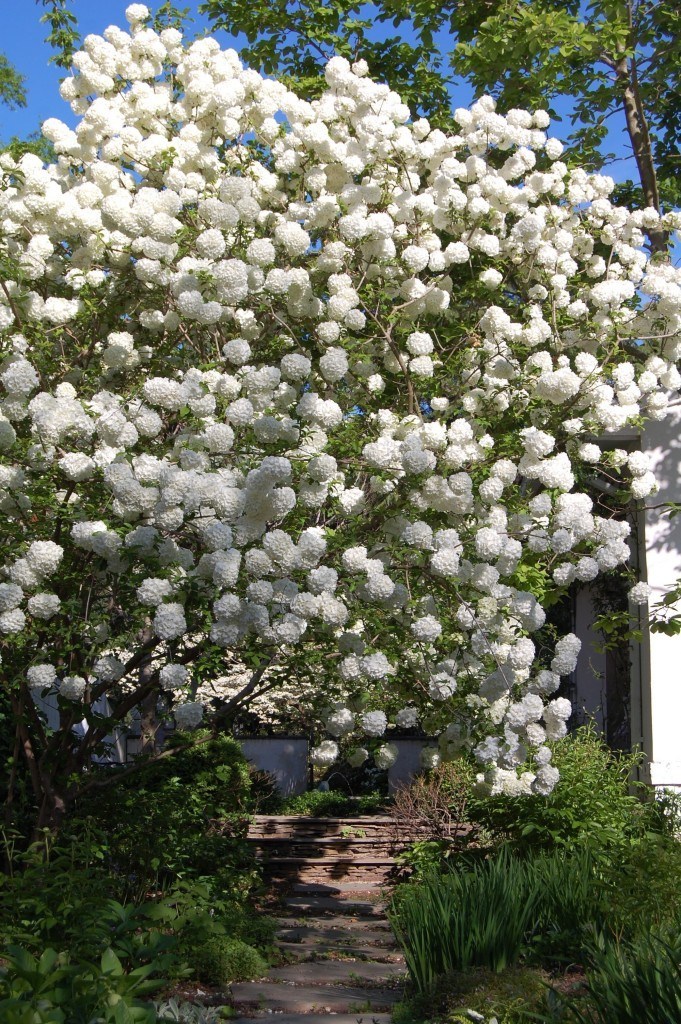
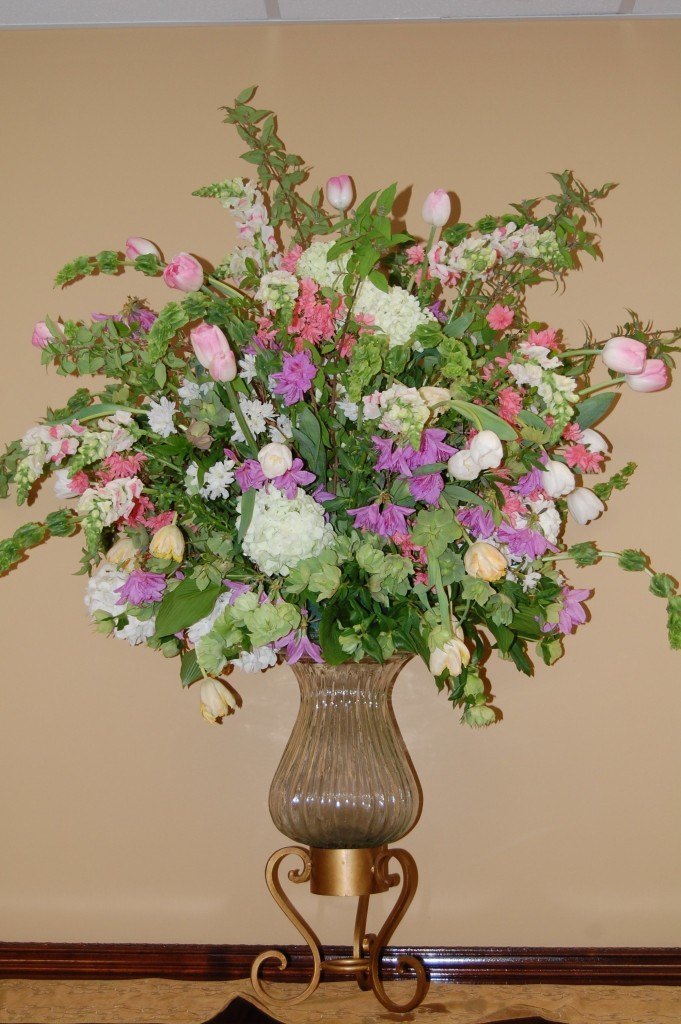 This arrangement welcomes spring in all its glory. Pink and peach Tulips, pink and lavender Azaleas, and pink Snapdragons blend beautifully with Snowball Viburnum (the OTHER Snowball Viburnum, Viburnum macrocephalum), Lenten Rose, Deutzia gracilis and greens.
This arrangement welcomes spring in all its glory. Pink and peach Tulips, pink and lavender Azaleas, and pink Snapdragons blend beautifully with Snowball Viburnum (the OTHER Snowball Viburnum, Viburnum macrocephalum), Lenten Rose, Deutzia gracilis and greens.



























